Vigil | Spot That Fire!
Team Updates
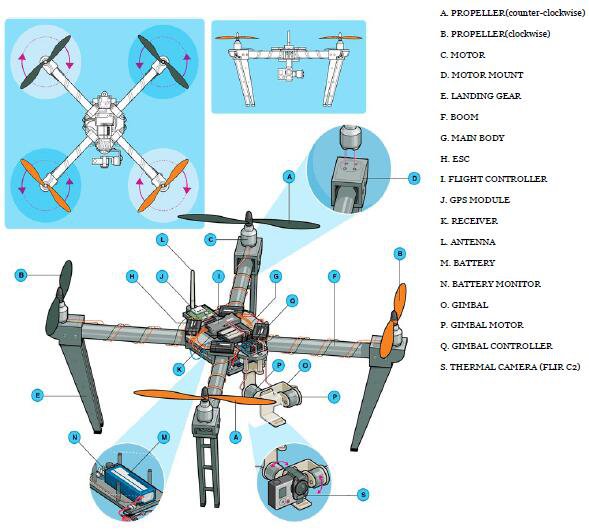
https://github.com/zyning/nasa-spaceapp-2018/blob/master/Drone.pdf

Vigil, a Latin word, means "watchman who alerts fireman in Rome
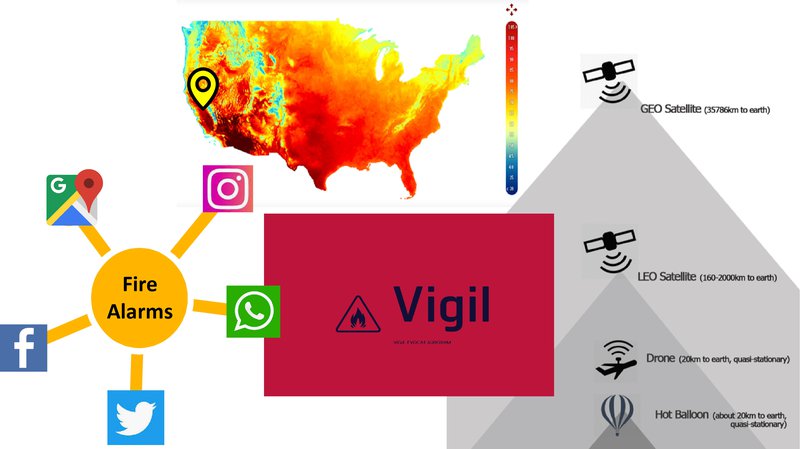
By improving connectivity between individuals, social medias, NASA's database, drones and other aircrafts, and firefighters, the wildfires can be detected within 10 s.
| """ | |
| This module contains various general utility functions. | |
| """ | |
| from __future__ import with_statement | |
| import logging | |
| logger = logging.getLogger('gensim.utils') | |
| try: | |
| from html.entities import name2codepoint as n2cp | |
| except ImportError: | |
| from htmlentitydefs import name2codepoint as n2cp | |
| try: | |
| import cPickle as _pickle | |
| except ImportError: | |
| import pickle as _pickle | |
| import re | |
| import unicodedata | |
| import os | |
| import random | |
| import itertools | |
| import tempfile | |
| from functools import wraps # for `synchronous` function lock | |
| import multiprocessing | |
| import shutil | |
| import sys | |
| import traceback | |
| from contextlib import contextmanager | |
| import numpy | |
| import scipy.sparse | |
| if sys.version_info[0] >= 3: | |
| unicode = str | |
| from six import iteritems, u, string_types | |
| from six.moves import xrange | |
| try: | |
| from pattern.en import parse | |
| logger.info("'pattern' package found; utils.lemmatize() is available for English") | |
| HAS_PATTERN = True | |
| except ImportError: | |
| HAS_PATTERN = False | |
| PAT_ALPHABETIC = re.compile('(((?![\d])\w)+)', re.UNICODE) | |
| RE_HTML_ENTITY = re.compile(r'&(#?)(x?)(\w+);', re.UNICODE) | |
| def synchronous(tlockname): | |
| """ | |
| A decorator to place an instance-based lock around a method. | |
| Adapted from http://code.activestate.com/recipes/577105-synchronization-decorator-for-class-methods/ | |
| """ | |
| def _synched(func): | |
| @wraps(func) | |
| def _synchronizer(self, *args, **kwargs): | |
| tlock = getattr(self, tlockname) | |
| logger.debug("acquiring lock %r for %s" % (tlockname, func.func_name)) | |
| with tlock: # use lock as a context manager to perform safe acquire/release pairs | |
| logger.debug("acquired lock %r for %s" % (tlockname, func.func_name)) | |
| result = func(self, *args, **kwargs) | |
| logger.debug("releasing lock %r for %s" % (tlockname, func.func_name)) | |
| return result | |
| return _synchronizer | |
| return _synched | |
| class NoCM(object): | |
| def acquire(self): | |
| pass | |
| def release(self): | |
| pass | |
| def __enter__(self): | |
| pass | |
| def __exit__(self, type, value, traceback): | |
| pass | |
| nocm = NoCM() | |
| @contextmanager | |
| def file_or_filename(input): | |
| """ | |
| Return a file-like object ready to be read from the beginning. `input` is either | |
| a filename (gz/bz2 also supported) or a file-like object supporting seek. | |
| """ | |
| if isinstance(input, string_types): | |
| # input was a filename: open as text file | |
| with smart_open(input) as fin: | |
| yield fin | |
| else: | |
| input.seek(0) | |
| yield input | |
| def deaccent(text): | |
| """ | |
| Remove accentuation from the given string. Input text is either a unicode string or utf8 encoded bytestring. | |
| Return input string with accents removed, as unicode. | |
| >>> deaccent("Šéf chomutovských komunistů dostal poštou bílý prášek") | |
| u'Sef chomutovskych komunistu dostal postou bily prasek' | |
| """ | |
| if not isinstance(text, unicode): | |
| # assume utf8 for byte strings, use default (strict) error handling | |
| text = text.decode('utf8') | |
| norm = unicodedata.normalize("NFD", text) | |
| result = u('').join(ch for ch in norm if unicodedata.category(ch) != 'Mn') | |
| return unicodedata.normalize("NFC", result) | |
| def copytree_hardlink(source, dest): | |
| """ | |
| Recursively copy a directory ala shutils.copytree, but hardlink files | |
| instead of copying. Available on UNIX systems only. | |
| """ | |
| copy2 = shutil.copy2 | |
| try: | |
| shutil.copy2 = os.link | |
| shutil.copytree(source, dest) | |
| finally: | |
| shutil.copy2 = copy2 | |
| def tokenize(text, lowercase=False, deacc=False, errors="strict", to_lower=False, lower=False): | |
| """ | |
| Iteratively yield tokens as unicode strings, optionally also lowercasing them | |
| and removing accent marks. | |
| Input text may be either unicode or utf8-encoded byte string. | |
| The tokens on output are maximal contiguous sequences of alphabetic | |
| characters (no digits!). | |
| >>> list(tokenize('Nic nemůže letět rychlostí vyšší, než 300 tisíc kilometrů za sekundu!', deacc = True)) | |
| [u'Nic', u'nemuze', u'letet', u'rychlosti', u'vyssi', u'nez', u'tisic', u'kilometru', u'za', u'sekundu'] | |
| """ | |
| lowercase = lowercase or to_lower or lower | |
| text = to_unicode(text, errors=errors) | |
| if lowercase: | |
| text = text.lower() | |
| if deacc: | |
| text = deaccent(text) | |
| for match in PAT_ALPHABETIC.finditer(text): | |
| yield match.group() | |
| def simple_preprocess(doc, deacc=False, min_len=2, max_len=15): | |
| """ | |
| Convert a document into a list of tokens. | |
| This lowercases, tokenizes, stems, normalizes etc. -- the output are final | |
| tokens = unicode strings, that won't be processed any further. | |
| """ | |
| tokens = [token for token in tokenize(doc, lower=True, deacc=deacc, errors='ignore') | |
| if min_len <= len(token) <= max_len and not token.startswith('_')] | |
| return tokens | |
| def any2utf8(text, errors='strict', encoding='utf8'): | |
| """Convert a string (unicode or bytestring in `encoding`), to bytestring in utf8.""" | |
| if isinstance(text, unicode): | |
| return text.encode('utf8') | |
| # do bytestring -> unicode -> utf8 full circle, to ensure valid utf8 | |
| return unicode(text, encoding, errors=errors).encode('utf8') | |
| to_utf8 = any2utf8 | |
| def any2unicode(text, encoding='utf8', errors='strict'): | |
| """Convert a string (bytestring in `encoding` or unicode), to unicode.""" | |
| if isinstance(text, unicode): | |
| return text | |
| return unicode(text, encoding, errors=errors) | |
| to_unicode = any2unicode | |
| class SaveLoad(object): | |
| """ | |
| Objects which inherit from this class have save/load functions, which un/pickle | |
| them to disk. | |
| This uses pickle for de/serializing, so objects must not contain | |
| unpicklable attributes, such as lambda functions etc. | |
| """ | |
| @classmethod | |
| def load(cls, fname, mmap=None): | |
| """ | |
| Load a previously saved object from file (also see `save`). | |
| If the object was saved with large arrays stored separately, you can load | |
| these arrays via mmap (shared memory) using `mmap='r'`. Default: don't use | |
| mmap, load large arrays as normal objects. | |
| """ | |
| logger.info("loading %s object from %s" % (cls.__name__, fname)) | |
| subname = lambda suffix: fname + '.' + suffix + '.npy' | |
| obj = unpickle(fname) | |
| for attrib in getattr(obj, '__numpys', []): | |
| logger.info("loading %s from %s with mmap=%s" % (attrib, subname(attrib), mmap)) | |
| setattr(obj, attrib, numpy.load(subname(attrib), mmap_mode=mmap)) | |
| for attrib in getattr(obj, '__scipys', []): | |
| logger.info("loading %s from %s with mmap=%s" % (attrib, subname(attrib), mmap)) | |
| sparse = unpickle(subname(attrib)) | |
| sparse.data = numpy.load(subname(attrib) + '.data.npy', mmap_mode=mmap) | |
| sparse.indptr = numpy.load(subname(attrib) + '.indptr.npy', mmap_mode=mmap) | |
| sparse.indices = numpy.load(subname(attrib) + '.indices.npy', mmap_mode=mmap) | |
| setattr(obj, attrib, sparse) | |
| for attrib in getattr(obj, '__ignoreds', []): | |
| logger.info("setting ignored attribute %s to None" % (attrib)) | |
| setattr(obj, attrib, None) | |
| return obj | |
| def save(self, fname, separately=None, sep_limit=10 * 1024**2, ignore=frozenset()): | |
| """ | |
| Save the object to file (also see `load`). | |
| If `separately` is None, automatically detect large numpy/scipy.sparse arrays | |
| in the object being stored, and store them into separate files. This avoids | |
| pickle memory errors and allows mmap'ing large arrays back on load efficiently. | |
| You can also set `separately` manually, in which case it must be a list of attribute | |
| names to be stored in separate files. The automatic check is not performed in this case. | |
| `ignore` is a set of attribute names to *not* serialize (file handles, caches etc). On | |
| subsequent load() these attributes will be set to None. | |
| """ | |
| logger.info("saving %s object under %s, separately %s" % (self.__class__.__name__, fname, separately)) | |
| subname = lambda suffix: fname + '.' + suffix + '.npy' | |
| tmp = {} | |
| if separately is None: | |
| separately = [] | |
| for attrib, val in iteritems(self.__dict__): | |
| if isinstance(val, numpy.ndarray) and val.size >= sep_limit: | |
| separately.append(attrib) | |
| elif isinstance(val, (scipy.sparse.csr_matrix, scipy.sparse.csc_matrix)) and val.nnz >= sep_limit: | |
| separately.append(attrib) | |
| # whatever's in `separately` or `ignore` at this point won't get pickled anymore | |
| for attrib in separately + list(ignore): | |
| if hasattr(self, attrib): | |
| tmp[attrib] = getattr(self, attrib) | |
| delattr(self, attrib) | |
| try: | |
| numpys, scipys, ignoreds = [], [], [] | |
| for attrib, val in iteritems(tmp): | |
| if isinstance(val, numpy.ndarray) and attrib not in ignore: | |
| numpys.append(attrib) | |
| logger.info("storing numpy array '%s' to %s" % (attrib, subname(attrib))) | |
| numpy.save(subname(attrib), numpy.ascontiguousarray(val)) | |
| elif isinstance(val, (scipy.sparse.csr_matrix, scipy.sparse.csc_matrix)) and attrib not in ignore: | |
| scipys.append(attrib) | |
| logger.info("storing scipy.sparse array '%s' under %s" % (attrib, subname(attrib))) | |
| numpy.save(subname(attrib) + '.data.npy', val.data) | |
| numpy.save(subname(attrib) + '.indptr.npy', val.indptr) | |
| numpy.save(subname(attrib) + '.indices.npy', val.indices) | |
| data, indptr, indices = val.data, val.indptr, val.indices | |
| val.data, val.indptr, val.indices = None, None, None | |
| try: | |
| pickle(val, subname(attrib)) # store array-less object | |
| finally: | |
| val.data, val.indptr, val.indices = data, indptr, indices | |
| else: | |
| logger.info("not storing attribute %s" % (attrib)) | |
| ignoreds.append(attrib) | |
| self.__dict__['__numpys'] = numpys | |
| self.__dict__['__scipys'] = scipys | |
| self.__dict__['__ignoreds'] = ignoreds | |
| pickle(self, fname) | |
| finally: | |
| # restore the attributes | |
| for attrib, val in iteritems(tmp): | |
| setattr(self, attrib, val) | |
| #endclass SaveLoad | |
| def identity(p): | |
| """Identity fnc, for flows that don't accept lambda (picking etc).""" | |
| return p | |
| def get_max_id(corpus): | |
| """ | |
| Return the highest feature id that appears in the corpus. | |
| For empty corpora (no features at all), return -1. | |
| """ | |
| maxid = -1 | |
| for document in corpus: | |
| maxid = max(maxid, max([-1] + [fieldid for fieldid, _ in document])) # [-1] to avoid exceptions from max(empty) | |
| return maxid | |
| class FakeDict(object): | |
| """ | |
| Objects of this class act as dictionaries that map integer->str(integer), for | |
| a specified range of integers <0, num_terms). | |
| This is meant to avoid allocating real dictionaries when `num_terms` is huge, which | |
| is a waste of memory. | |
| """ | |
| def __init__(self, num_terms): | |
| self.num_terms = num_terms | |
| def __str__(self): | |
| return "FakeDict(num_terms=%s)" % self.num_terms | |
| def __getitem__(self, val): | |
| if 0 <= val < self.num_terms: | |
| return str(val) | |
| raise ValueError("internal id out of bounds (%s, expected <0..%s))" % | |
| (val, self.num_terms)) | |
| def iteritems(self): | |
| for i in xrange(self.num_terms): | |
| yield i, str(i) | |
| def keys(self): | |
| """ | |
| Override the dict.keys() function, which is used to determine the maximum | |
| internal id of a corpus = the vocabulary dimensionality. | |
| HACK: To avoid materializing the whole `range(0, self.num_terms)`, this returns | |
| the highest id = `[self.num_terms - 1]` only. | |
| """ | |
| return [self.num_terms - 1] | |
| def __len__(self): | |
| return self.num_terms | |
| def get(self, val, default=None): | |
| if 0 <= val < self.num_terms: | |
| return str(val) | |
| return default | |
| def dict_from_corpus(corpus): | |
| """ | |
| Scan corpus for all word ids that appear in it, then construct and return a mapping | |
| which maps each ``wordId -> str(wordId)``. | |
| This function is used whenever *words* need to be displayed (as opposed to just | |
| their ids) but no wordId->word mapping was provided. The resulting mapping | |
| only covers words actually used in the corpus, up to the highest wordId found. | |
| """ | |
| num_terms = 1 + get_max_id(corpus) | |
| id2word = FakeDict(num_terms) | |
| return id2word | |
| def is_corpus(obj): | |
| """ | |
| Check whether `obj` is a corpus. Return (is_corpus, new) 2-tuple, where | |
| `new is obj` if `obj` was an iterable, or `new` yields the same sequence as | |
| `obj` if it was an iterator. | |
| `obj` is a corpus if it supports iteration over documents, where a document | |
| is in turn anything that acts as a sequence of 2-tuples (int, float). | |
| Note: An "empty" corpus (empty input sequence) is ambiguous, so in this case the | |
| result is forcefully defined as `is_corpus=False`. | |
| """ | |
| try: | |
| if 'Corpus' in obj.__class__.__name__: # the most common case, quick hack | |
| return True, obj | |
| except: | |
| pass | |
| try: | |
| if hasattr(obj, 'next'): | |
| # the input is an iterator object, meaning once we call next() | |
| # that element could be gone forever. we must be careful to put | |
| # whatever we retrieve back again | |
| doc1 = next(obj) | |
| obj = itertools.chain([doc1], obj) | |
| else: | |
| doc1 = next(iter(obj)) # empty corpus is resolved to False here | |
| if len(doc1) == 0: # sparse documents must have a __len__ function (list, tuple...) | |
| return True, obj # the first document is empty=>assume this is a corpus | |
| id1, val1 = next(iter(doc1)) # if obj is a numpy array, it resolves to False here | |
| id1, val1 = int(id1), float(val1) # must be a 2-tuple (integer, float) | |
| except: | |
| return False, obj | |
| return True, obj | |
| def get_my_ip(): | |
| """ | |
| Try to obtain our external ip (from the pyro nameserver's point of view) | |
| This tries to sidestep the issue of bogus `/etc/hosts` entries and other | |
| local misconfigurations, which often mess up hostname resolution. | |
| If all else fails, fall back to simple `socket.gethostbyname()` lookup. | |
| """ | |
| import socket | |
| try: | |
| import Pyro4 | |
| # we know the nameserver must exist, so use it as our anchor point | |
| ns = Pyro4.naming.locateNS() | |
| s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM) | |
| s.connect((ns._pyroUri.host, ns._pyroUri.port)) | |
| result, port = s.getsockname() | |
| except: | |
| try: | |
| # see what ifconfig says about our default interface | |
| import commands | |
| result = commands.getoutput("ifconfig").split("\n")[1].split()[1][5:] | |
| if len(result.split('.')) != 4: | |
| raise Exception() | |
| except: | |
| # give up, leave the resolution to gethostbyname | |
| result = socket.gethostbyname(socket.gethostname()) | |
| return result | |
| class RepeatCorpus(SaveLoad): | |
| """ | |
| Used in the tutorial on distributed computing and likely not useful anywhere else. | |
| """ | |
| def __init__(self, corpus, reps): | |
| """ | |
| Wrap a `corpus` as another corpus of length `reps`. This is achieved by | |
| repeating documents from `corpus` over and over again, until the requested | |
| length `len(result)==reps` is reached. Repetition is done | |
| on-the-fly=efficiently, via `itertools`. | |
| >>> corpus = [[(1, 0.5)], []] # 2 documents | |
| >>> list(RepeatCorpus(corpus, 5)) # repeat 2.5 times to get 5 documents | |
| [[(1, 0.5)], [], [(1, 0.5)], [], [(1, 0.5)]] | |
| """ | |
| self.corpus = corpus | |
| self.reps = reps | |
| def __iter__(self): | |
| return itertools.islice(itertools.cycle(self.corpus), self.reps) | |
| class ClippedCorpus(SaveLoad): | |
| def __init__(self, corpus, max_docs=None): | |
| """ | |
| Return a corpus that is the "head" of input iterable `corpus`. | |
| Any documents after `max_docs` are ignored. This effectively limits the | |
| length of the returned corpus to <= `max_docs`. Set `max_docs=None` for | |
| "no limit", effectively wrapping the entire input corpus. | |
| """ | |
| self.corpus = corpus | |
| self.max_docs = max_docs | |
| def __iter__(self): | |
| return itertools.islice(self.corpus, self.max_docs) | |
| def __len__(self): | |
| return min(self.max_docs, len(self.corpus)) | |
| def decode_htmlentities(text): | |
| """ | |
| Decode HTML entities in text, coded as hex, decimal or named. | |
| Adapted from http://github.com/sku/python-twitter-ircbot/blob/321d94e0e40d0acc92f5bf57d126b57369da70de/html_decode.py | |
| >>> u = u'E tu vivrai nel terrore - L'aldilà (1981)' | |
| >>> print(decode_htmlentities(u).encode('UTF-8')) | |
| E tu vivrai nel terrore - L'aldilà (1981) | |
| >>> print(decode_htmlentities("l'eau")) | |
| l'eau | |
| >>> print(decode_htmlentities("foo < bar")) | |
| foo < bar | |
| """ | |
| def substitute_entity(match): | |
| ent = match.group(3) | |
| if match.group(1) == "#": | |
| # decoding by number | |
| if match.group(2) == '': | |
| # number is in decimal | |
| return unichr(int(ent)) | |
| elif match.group(2) == 'x': | |
| # number is in hex | |
| return unichr(int('0x' + ent, 16)) | |
| else: | |
| # they were using a name | |
| cp = n2cp.get(ent) | |
| if cp: | |
| return unichr(cp) | |
| else: | |
| return match.group() | |
| try: | |
| return RE_HTML_ENTITY.sub(substitute_entity, text) | |
| except: | |
| # in case of errors, return input | |
| # e.g., ValueError: unichr() arg not in range(0x10000) (narrow Python build) | |
| return text | |
| def chunkize_serial(iterable, chunksize, as_numpy=False): | |
| """ | |
| Return elements from the iterable in `chunksize`-ed lists. The last returned | |
| element may be smaller (if length of collection is not divisible by `chunksize`). | |
| >>> print(list(grouper(range(10), 3))) | |
| [[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8], [9]] | |
| """ | |
| import numpy | |
| it = iter(iterable) | |
| while True: | |
| if as_numpy: | |
| # convert each document to a 2d numpy array (~6x faster when transmitting | |
| # chunk data over the wire, in Pyro) | |
| wrapped_chunk = [[numpy.array(doc) for doc in itertools.islice(it, int(chunksize))]] | |
| else: | |
| wrapped_chunk = [list(itertools.islice(it, int(chunksize)))] | |
| if not wrapped_chunk[0]: | |
| break | |
| # memory opt: wrap the chunk and then pop(), to avoid leaving behind a dangling reference | |
| yield wrapped_chunk.pop() | |
| grouper = chunkize_serial | |
| class InputQueue(multiprocessing.Process): | |
| def __init__(self, q, corpus, chunksize, maxsize, as_numpy): | |
| super(InputQueue, self).__init__() | |
| self.q = q | |
| self.maxsize = maxsize | |
| self.corpus = corpus | |
| self.chunksize = chunksize | |
| self.as_numpy = as_numpy | |
| def run(self): | |
| if self.as_numpy: | |
| import numpy # don't clutter the global namespace with a dependency on numpy | |
| it = iter(self.corpus) | |
| while True: | |
| chunk = itertools.islice(it, self.chunksize) | |
| if self.as_numpy: | |
| # HACK XXX convert documents to numpy arrays, to save memory. | |
| # This also gives a scipy warning at runtime: | |
| # "UserWarning: indices array has non-integer dtype (float64)" | |
| wrapped_chunk = [[numpy.asarray(doc) for doc in chunk]] | |
| else: | |
| wrapped_chunk = [list(chunk)] | |
| if not wrapped_chunk[0]: | |
| self.q.put(None, block=True) | |
| break | |
| try: | |
| qsize = self.q.qsize() | |
| except NotImplementedError: | |
| qsize = '?' | |
| logger.debug("prepared another chunk of %i documents (qsize=%s)" % | |
| (len(wrapped_chunk[0]), qsize)) | |
| self.q.put(wrapped_chunk.pop(), block=True) | |
| #endclass InputQueue | |
| if os.name == 'nt': | |
| logger.info("detected Windows; aliasing chunkize to chunkize_serial") | |
| def chunkize(corpus, chunksize, maxsize=0, as_numpy=False): | |
| for chunk in chunkize_serial(corpus, chunksize, as_numpy=as_numpy): | |
| yield chunk | |
| else: | |
| def chunkize(corpus, chunksize, maxsize=0, as_numpy=False): | |
| """ | |
| Split a stream of values into smaller chunks. | |
| Each chunk is of length `chunksize`, except the last one which may be smaller. | |
| A once-only input stream (`corpus` from a generator) is ok, chunking is done | |
| efficiently via itertools. | |
| If `maxsize > 1`, don't wait idly in between successive chunk `yields`, but | |
| rather keep filling a short queue (of size at most `maxsize`) with forthcoming | |
| chunks in advance. This is realized by starting a separate process, and is | |
| meant to reduce I/O delays, which can be significant when `corpus` comes | |
| from a slow medium (like harddisk). | |
| If `maxsize==0`, don't fool around with parallelism and simply yield the chunksize | |
| via `chunkize_serial()` (no I/O optimizations). | |
| >>> for chunk in chunkize(range(10), 4): print(chunk) | |
| [0, 1, 2, 3] | |
| [4, 5, 6, 7] | |
| [8, 9] | |
| """ | |
| assert chunksize > 0 | |
| if maxsize > 0: | |
| q = multiprocessing.Queue(maxsize=maxsize) | |
| worker = InputQueue(q, corpus, chunksize, maxsize=maxsize, as_numpy=as_numpy) | |
| worker.daemon = True | |
| worker.start() | |
| while True: | |
| chunk = [q.get(block=True)] | |
| if chunk[0] is None: | |
| break | |
| yield chunk.pop() | |
| else: | |
| for chunk in chunkize_serial(corpus, chunksize, as_numpy=as_numpy): | |
| yield chunk | |
| def make_closing(base, **attrs): | |
| """ | |
| Add support for `with Base(attrs) as fout:` to the base class if it's missing. | |
| The base class' `close()` method will be called on context exit, to always close the file properly. | |
| This is needed for gzip.GzipFile, bz2.BZ2File etc in older Pythons (<=2.6), which otherwise | |
| raise "AttributeError: GzipFile instance has no attribute '__exit__'". | |
| """ | |
| if not hasattr(base, '__enter__'): | |
| attrs['__enter__'] = lambda self: self | |
| if not hasattr(base, '__exit__'): | |
| attrs['__exit__'] = lambda self, type, value, traceback: self.close() | |
| return type('Closing' + base.__name__, (base, object), attrs) | |
| def smart_open(fname, mode='rb'): | |
| _, ext = os.path.splitext(fname) | |
| if ext == '.bz2': | |
| from bz2 import BZ2File | |
| return make_closing(BZ2File)(fname, mode) | |
| if ext == '.gz': | |
| from gzip import GzipFile | |
| return make_closing(GzipFile)(fname, mode) | |
| return open(fname, mode) | |
| def pickle(obj, fname, protocol=-1): | |
| """Pickle object `obj` to file `fname`.""" | |
| with smart_open(fname, 'wb') as fout: # 'b' for binary, needed on Windows | |
| _pickle.dump(obj, fout, protocol=protocol) | |
| def unpickle(fname): | |
| """Load pickled object from `fname`""" | |
| with smart_open(fname) as f: | |
| return _pickle.load(f) | |
| def revdict(d): | |
| """ | |
| Reverse a dictionary mapping. | |
| When two keys map to the same value, only one of them will be kept in the | |
| result (which one is kept is arbitrary). | |
| """ | |
| return dict((v, k) for (k, v) in iteritems(d)) | |
| def toptexts(query, texts, index, n=10): | |
| """ | |
| Debug fnc to help inspect the top `n` most similar documents (according to a | |
| similarity index `index`), to see if they are actually related to the query. | |
| `texts` is any object that can return something insightful for each document | |
| via `texts[docid]`, such as its fulltext or snippet. | |
| Return a list of 3-tuples (docid, doc's similarity to the query, texts[docid]). | |
| """ | |
| sims = index[query] # perform a similarity query against the corpus | |
| sims = sorted(enumerate(sims), key=lambda item: -item[1]) | |
| result = [] | |
| for topid, topcosine in sims[:n]: # only consider top-n most similar docs | |
| result.append((topid, topcosine, texts[topid])) | |
| return result | |
| def randfname(prefix='gensim'): | |
| randpart = hex(random.randint(0, 0xffffff))[2:] | |
| return os.path.join(tempfile.gettempdir(), prefix + randpart) | |
| def upload_chunked(server, docs, chunksize=1000, preprocess=None): | |
| """ | |
| Memory-friendly upload of documents to a SimServer (or Pyro SimServer proxy). | |
| Use this function to train or index large collections -- avoid sending the | |
| entire corpus over the wire as a single Pyro in-memory object. The documents | |
| will be sent in smaller chunks, of `chunksize` documents each. | |
| """ | |
| start = 0 | |
| for chunk in grouper(docs, chunksize): | |
| end = start + len(chunk) | |
| logger.info("uploading documents %i-%i" % (start, end - 1)) | |
| if preprocess is not None: | |
| pchunk = [] | |
| for doc in chunk: | |
| doc['tokens'] = preprocess(doc['text']) | |
| del doc['text'] | |
| pchunk.append(doc) | |
| chunk = pchunk | |
| server.buffer(chunk) | |
| start = end | |
| def getNS(): | |
| """ | |
| Return a Pyro name server proxy. If there is no name server running, | |
| start one on 0.0.0.0 (all interfaces), as a background process. | |
| """ | |
| import Pyro4 | |
| try: | |
| return Pyro4.locateNS() | |
| except Pyro4.errors.NamingError: | |
| logger.info("Pyro name server not found; starting a new one") | |
| os.system("python -m Pyro4.naming -n 0.0.0.0 &") | |
| # TODO: spawn a proper daemon ala http://code.activestate.com/recipes/278731/ ? | |
| # like this, if there's an error somewhere, we'll never know... (and the loop | |
| # below will block). And it probably doesn't work on windows, either. | |
| while True: | |
| try: | |
| return Pyro4.locateNS() | |
| except: | |
| pass | |
| def pyro_daemon(name, obj, random_suffix=False, ip=None, port=None): | |
| """ | |
| Register object with name server (starting the name server if not running | |
| yet) and block until the daemon is terminated. The object is registered under | |
| `name`, or `name`+ some random suffix if `random_suffix` is set. | |
| """ | |
| if random_suffix: | |
| name += '.' + hex(random.randint(0, 0xffffff))[2:] | |
| import Pyro4 | |
| with getNS() as ns: | |
| with Pyro4.Daemon(ip or get_my_ip(), port or 0) as daemon: | |
| # register server for remote access | |
| uri = daemon.register(obj, name) | |
| ns.remove(name) | |
| ns.register(name, uri) | |
| logger.info("%s registered with nameserver (URI '%s')" % (name, uri)) | |
| daemon.requestLoop() | |
| if HAS_PATTERN: | |
| def lemmatize(content, allowed_tags=re.compile('(NN|VB|JJ|RB)'), light=False, stopwords=frozenset()): | |
| """ | |
| This function is only available when the optional 'pattern' package is installed. | |
| Use the English lemmatizer from `pattern` to extract tokens in | |
| their base form=lemma, e.g. "are, is, being" -> "be" etc. | |
| This is a smarter version of stemming, taking word context into account. | |
| Only considers nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs by default (=all other lemmas are discarded). | |
| >>> lemmatize('Hello World! How is it going?! Nonexistentword, 21') | |
| ['world/NN', 'be/VB', 'go/VB', 'nonexistentword/NN'] | |
| >>> lemmatize('The study ranks high.') | |
| ['study/NN', 'rank/VB', 'high/JJ'] | |
| >>> lemmatize('The ranks study hard.') | |
| ['rank/NN', 'study/VB', 'hard/RB'] | |
| """ | |
| if light: | |
| import warnings | |
| warnings.warn("The light flag is no longer supported by pattern.") | |
| # tokenization in `pattern` is weird; it gets thrown off by non-letters, | |
| # producing '==relate/VBN' or '**/NN'... try to preprocess the text a little | |
| # FIXME this throws away all fancy parsing cues, including sentence structure, | |
| # abbreviations etc. | |
| content = u(' ').join(tokenize(content, lower=True, errors='ignore')) | |
| parsed = parse(content, lemmata=True, collapse=False) | |
| result = [] | |
| for sentence in parsed: | |
| for token, tag, _, _, lemma in sentence: | |
| if 2 <= len(lemma) <= 15 and not lemma.startswith('_') and lemma not in stopwords: | |
| if allowed_tags.match(tag): | |
| lemma += "/" + tag[:2] | |
| result.append(lemma.encode('utf8')) | |
| return result |
P
Pengyuan Liu| mport logging | |
| import word2vecReaderUtils as utils | |
| from numpy import exp, dot, zeros, outer, random, dtype, float32 as REAL,\ | |
| uint32, seterr, array, uint8, vstack, argsort, fromstring, sqrt, newaxis,\ | |
| ndarray, empty, sum as np_sum, prod | |
| from six import string_types | |
| from gensim import matutils | |
| class Vocab(object): | |
| """A single vocabulary item, used internally for constructing binary trees (incl. both word leaves and inner nodes).""" | |
| def __init__(self, **kwargs): | |
| self.count = 0 | |
| self.__dict__.update(kwargs) | |
| def __lt__(self, other): # used for sorting in a priority queue | |
| return self.count < other.count | |
| def __str__(self): | |
| vals = ['%s:%r' % (key, self.__dict__[key]) for key in sorted(self.__dict__) if not key.startswith('_')] | |
| return "<" + ', '.join(vals) + ">" | |
| class Word2Vec: | |
| """ | |
| Class for training, using and evaluating neural networks described in https://code.google.com/p/word2vec/ | |
| The model can be stored/loaded via its `save()` and `load()` methods, or stored/loaded in a format | |
| compatible with the original word2vec implementation via `save_word2vec_format()` and `load_word2vec_format()`. | |
| """ | |
| def __init__(self, sentences=None, size=100, alpha=0.025, window=5, min_count=5, | |
| sample=0, seed=1, workers=1, min_alpha=0.0001, sg=1, hs=1, negative=0, cbow_mean=0): | |
| """ | |
| Initialize the model from an iterable of `sentences`. Each sentence is a | |
| list of words (unicode strings) that will be used for training. | |
| The `sentences` iterable can be simply a list, but for larger corpora, | |
| consider an iterable that streams the sentences directly from disk/network. | |
| See :class:`BrownCorpus`, :class:`Text8Corpus` or :class:`LineSentence` in | |
| this module for such examples. | |
| If you don't supply `sentences`, the model is left uninitialized -- use if | |
| you plan to initialize it in some other way. | |
| `sg` defines the training algorithm. By default (`sg=1`), skip-gram is used. Otherwise, `cbow` is employed. | |
| `size` is the dimensionality of the feature vectors. | |
| `window` is the maximum distance between the current and predicted word within a sentence. | |
| `alpha` is the initial learning rate (will linearly drop to zero as training progresses). | |
| `seed` = for the random number generator. | |
| `min_count` = ignore all words with total frequency lower than this. | |
| `sample` = threshold for configuring which higher-frequency words are randomly downsampled; | |
| default is 0 (off), useful value is 1e-5. | |
| `workers` = use this many worker threads to train the model (=faster training with multicore machines). | |
| `hs` = if 1 (default), hierarchical sampling will be used for model training (else set to 0). | |
| `negative` = if > 0, negative sampling will be used, the int for negative | |
| specifies how many "noise words" should be drawn (usually between 5-20). | |
| `cbow_mean` = if 0 (default), use the sum of the context word vectors. If 1, use the mean. | |
| Only applies when cbow is used. | |
| """ | |
| self.vocab = {} # mapping from a word (string) to a Vocab object | |
| self.index2word = [] # map from a word's matrix index (int) to word (string) | |
| self.sg = int(sg) | |
| self.table = None # for negative sampling --> this needs a lot of RAM! consider setting back to None before saving | |
| self.layer1_size = int(size) | |
| #if size % 4 != 0: | |
| # logger.warning("consider setting layer size to a multiple of 4 for greater performance") | |
| self.alpha = float(alpha) | |
| self.window = int(window) | |
| self.seed = seed | |
| self.min_count = min_count | |
| self.sample = sample | |
| self.workers = workers | |
| self.min_alpha = min_alpha | |
| self.hs = hs | |
| self.negative = negative | |
| self.cbow_mean = int(cbow_mean) | |
| if sentences is not None: | |
| self.build_vocab(sentences) | |
| self.train(sentences) | |
| @classmethod | |
| def load_word2vec_format(cls, fname, fvocab=None, binary=False, norm_only=True): | |
| """ | |
| Load the input-hidden weight matrix from the original C word2vec-tool format. | |
| Note that the information stored in the file is incomplete (the binary tree is missing), | |
| so while you can query for word similarity etc., you cannot continue training | |
| with a model loaded this way. | |
| `binary` is a boolean indicating whether the data is in binary word2vec format. | |
| `norm_only` is a boolean indicating whether to only store normalised word2vec vectors in memory. | |
| Word counts are read from `fvocab` filename, if set (this is the file generated | |
| by `-save-vocab` flag of the original C tool). | |
| """ | |
| counts = None | |
| if fvocab is not None: | |
| #logger.info("loading word counts from %s" % (fvocab)) | |
| counts = {} | |
| with utils.smart_open(fvocab) as fin: | |
| for line in fin: | |
| word, count = utils.to_unicode(line).strip().split() | |
| counts[word] = int(count) | |
| #logger.info("loading projection weights from %s" % (fname)) | |
| with utils.smart_open(fname) as fin: | |
| header = utils.to_unicode(fin.readline()) | |
| vocab_size, layer1_size = map(int, header.split()) # throws for invalid file format | |
| result = Word2Vec(size=layer1_size) | |
| result.syn0 = zeros((vocab_size, layer1_size), dtype=REAL) | |
| if binary: | |
| binary_len = dtype(REAL).itemsize * layer1_size | |
| for line_no in range(vocab_size): | |
| # mixed text and binary: read text first, then binary | |
| word = [] | |
| while True: | |
| ch = fin.read(1) | |
| if ch == b' ': | |
| break | |
| if ch != b'\n': # ignore newlines in front of words (some binary files have newline, some don't) | |
| word.append(ch) | |
| word = utils.to_unicode(b''.join(word),encoding='latin-1') | |
| if counts is None: | |
| result.vocab[word] = Vocab(index=line_no, count=vocab_size - line_no) | |
| elif word in counts: | |
| result.vocab[word] = Vocab(index=line_no, count=counts[word]) | |
| else: | |
| #logger.warning("vocabulary file is incomplete") | |
| result.vocab[word] = Vocab(index=line_no, count=None) | |
| result.index2word.append(word) | |
| result.syn0[line_no] = fromstring(fin.read(binary_len), dtype=REAL) | |
| else: | |
| for line_no, line in enumerate(fin): | |
| parts = utils.to_unicode(line).split() | |
| if len(parts) != layer1_size + 1: | |
| raise ValueError("invalid vector on line %s (is this really the text format?)" % (line_no)) | |
| word, weights = parts[0], map(REAL, parts[1:]) | |
| if counts is None: | |
| result.vocab[word] = Vocab(index=line_no, count=vocab_size - line_no) | |
| elif word in counts: | |
| result.vocab[word] = Vocab(index=line_no, count=counts[word]) | |
| else: | |
| #logger.warning("vocabulary file is incomplete") | |
| result.vocab[word] = Vocab(index=line_no, count=None) | |
| result.index2word.append(word) | |
| result.syn0[line_no] = weights | |
| #logger.info("loaded %s matrix from %s" % (result.syn0.shape, fname)) | |
| result.init_sims(norm_only) | |
| return result | |
| def init_sims(self, replace=False): | |
| """ | |
| Precompute L2-normalized vectors. | |
| If `replace` is set, forget the original vectors and only keep the normalized | |
| ones = saves lots of memory! | |
| Note that you **cannot continue training** after doing a replace. The model becomes | |
| effectively read-only = you can call `most_similar`, `similarity` etc., but not `train`. | |
| """ | |
| if getattr(self, 'syn0norm', None) is None or replace: | |
| #logger.info("precomputing L2-norms of word weight vectors") | |
| if replace: | |
| for i in range(self.syn0.shape[0]): | |
| self.syn0[i, :] /= sqrt((self.syn0[i, :] ** 2).sum(-1)) | |
| self.syn0norm = self.syn0 | |
| if hasattr(self, 'syn1'): | |
| del self.syn1 | |
| else: | |
| self.syn0norm = (self.syn0 / sqrt((self.syn0 ** 2).sum(-1))[..., newaxis]).astype(REAL) | |
| def __getitem__(self, word): | |
| return self.syn0[self.vocab[word].index] | |
| def __contains__(self, word): | |
| return word in self.vocab | |
| def most_similar(self, positive=[], negative=[], topn=10): | |
| if isinstance(positive, string_types) and not negative: | |
| # allow calls like most_similar('dog'), as a shorthand for most_similar(['dog']) | |
| positive = [positive] | |
| # add weights for each word, if not already present; default to 1.0 for positive and -1.0 for negative words | |
| positive = [(word, 1.0) if isinstance(word, string_types + (ndarray,)) | |
| else word for word in positive] | |
| negative = [(word, -1.0) if isinstance(word, string_types + (ndarray,)) | |
| else word for word in negative] | |
| # compute the weighted average of all words | |
| all_words, mean = set(), [] | |
| for word, weight in positive + negative: | |
| if isinstance(word, ndarray): | |
| mean.append(weight * word) | |
| elif word in self.vocab: | |
| mean.append(weight * self.syn0norm[self.vocab[word].index]) | |
| all_words.add(self.vocab[word].index) | |
| else: | |
| raise KeyError("word '%s' not in vocabulary" % word) | |
| if not mean: | |
| raise ValueError("cannot compute similarity with no input") | |
| mean = matutils.unitvec(array(mean).mean(axis=0)).astype(REAL) | |
| dists = dot(self.syn0norm, mean) | |
| if not topn: | |
| return dists | |
| best = argsort(dists)[::-1][:topn + len(all_words)] | |
| # ignore (don't return) words from the input | |
| result = [(self.index2word[sim], float(dists[sim]), self.syn0[sim]) for sim in best if sim not in all_words] | |
| return result[:topn] | |
| def most_similar_cosmul(self, positive=[], negative=[], topn=10): | |
| self.init_sims() | |
| if isinstance(positive, string_types) and not negative: | |
| # allow calls like most_similar_cosmul('dog'), as a shorthand for most_similar_cosmul(['dog']) | |
| positive = [positive] | |
| all_words = set() | |
| def word_vec(word): | |
| if isinstance(word, ndarray): | |
| return word | |
| elif word in self.vocab: | |
| all_words.add(self.vocab[word].index) | |
| return self.syn0norm[self.vocab[word].index] | |
| else: | |
| raise KeyError("word '%s' not in vocabulary" % word) | |
| positive = [word_vec(word) for word in positive] | |
| negative = [word_vec(word) for word in negative] | |
| if not positive: | |
| raise ValueError("cannot compute similarity with no input") | |
| # equation (4) of Levy & Goldberg "Linguistic Regularities...", | |
| # with distances shifted to [0,1] per footnote (7) | |
| pos_dists = [((1 + dot(self.syn0norm, term)) / 2) for term in positive] | |
| neg_dists = [((1 + dot(self.syn0norm, term)) / 2) for term in negative] | |
| dists = prod(pos_dists, axis=0) / (prod(neg_dists, axis=0) + 0.000001) | |
| if not topn: | |
| return dists | |
| best = argsort(dists)[::-1][:topn + len(all_words)] | |
| # ignore (don't return) words from the input | |
| result = [(self.index2word[sim], float(dists[sim],)) for sim in best if sim not in all_words] | |
| return result[:topn] | |
| if __name__ == "__main__": | |
| model_path = "./word2vec_twitter_model.bin" | |
| print("Loading the model, this can take some time...") | |
| model = Word2Vec.load_word2vec_format(model_path, binary=True) | |
| print("The vocabulary size is: "+str(len(model.vocab))) |
P
Pengyuan Liu| importpandasaspd | |
| importos | |
| list_path= [] | |
| os.chdir("/home/pengyuan/PycharmProjects/NASA_2018/") | |
| forroot, dirs, filesinos.walk(".", topdown=False): | |
| fornameinfiles: | |
| file_path=os.path.join(root, name) | |
| list_path.append(file_path) | |
| print(list_path) | |
| # for name in dirs: | |
| # print(os.path.join(root, name)) | |
| df=pd.DataFrame(list_path) | |
| df.to_csv('./image_path.csv') |
P
Pengyuan Liu| from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer | |
| from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences | |
| from keras.layers import Embedding, Input, LSTM, RepeatVector, Dense, Dropout,concatenate,Conv2D,UpSampling2D,MaxPooling2D,BatchNormalization,Activation,Add,GlobalMaxPool2D,Flatten | |
| from keras.models import Model | |
| import keras.backend as K | |
| from keras.utils import plot_model | |
| from IPython.display import Image | |
| import pandas as pd | |
| import cv2 | |
| from word2vecReader import Word2Vec | |
| import numpy as np | |
| from keras.utils import to_categorical | |
| import keras | |
| df = pd.read_csv('/home/pengyuan/PycharmProjects/NASA_2018/train.csv') | |
| df_2 = pd.read_csv('/home/pengyuan/PycharmProjects/NASA_2018/test.csv') | |
| label = to_categorical(df['labels'].values) | |
| print(label.shape) | |
| label_2 = to_categorical(df_2['labels'].values) | |
| def process_images(df, final_shape=(158, 158)): | |
| # Set up array. | |
| X = [] | |
| # Get each filename, read, resize, and append to X. | |
| for file in df.image: | |
| try: | |
| image = cv2.resize(cv2.imread(file), final_shape) | |
| except: | |
| print(file) | |
| X.append(image) | |
| # Normalize the array as a float. | |
| X = np.asarray(X) | |
| X = X.reshape(X.shape[0],158,158,3) | |
| X = X / 255. | |
| return X | |
| text = [] | |
| text_ = [] | |
| text_test = [] | |
| text_test_ = [ ] | |
| text.append(df['text'].values) | |
| for tweet in text: | |
| for t in tweet: | |
| text_.append(t) | |
| print(text_) | |
| text_test.append(df_2['text'].values) | |
| for tweet in text_test: | |
| for t in tweet: | |
| text_test_.append(t) | |
| print(text_test_) | |
| all_sentences_test = text_test_ | |
| tokenizer_test = Tokenizer() # nb_words=MAX_NB_WORDS | |
| tokenizer_test.fit_on_texts(all_sentences_test) | |
| sequences_test = tokenizer_test.texts_to_sequences(all_sentences_test) | |
| word_index_test = tokenizer_test.word_index | |
| print('Found %s unique tokens.' % len(word_index_test)) | |
| x_test = pad_sequences(sequences_test,maxlen=12) | |
| print(x_test.shape) | |
| all_sentences = text_ | |
| tokenizer = Tokenizer() # nb_words=MAX_NB_WORDS | |
| tokenizer.fit_on_texts(all_sentences) | |
| sequences = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(all_sentences) | |
| word_index = tokenizer.word_index | |
| print('Found %s unique tokens.' % len(word_index)) | |
| x_train = pad_sequences(sequences) | |
| print(x_train.shape) | |
| model = Word2Vec.load_word2vec_format("/home/pengyuan/PycharmProjects/Multimodal_Study/Twitter_word2vec/word2vec_twitter_model.bin",binary=True) | |
| pretrained_weights = model.syn0 | |
| vocab_size, emdedding_size = pretrained_weights.shape | |
| print(vocab_size, emdedding_size) | |
| embedding_matrix = np.zeros((len(word_index) + 1, 400)) | |
| for word, i in word_index.items(): | |
| if word in model: | |
| embedding_matrix[i] = model[word] | |
| else: | |
| embedding_matrix[i] = np.random.rand(1, 400)[0] | |
| image_data = process_images(df) | |
| print(image_data.shape) | |
| image_data_test = process_images(df_2) | |
| Input_text = Input(shape=(12,)) | |
| Input_image = Input(shape=(158,158,3)) | |
| embedding_layer = Embedding(len(word_index) + 1, | |
| 400, | |
| weights=[embedding_matrix], | |
| input_length=12, | |
| trainable=False) | |
| embedded_sequences = embedding_layer(Input_text) | |
| encoded_text = LSTM(32)(embedded_sequences) | |
| encoded_img = Conv2D(128,(3,3),activation='relu',padding='same')(Input_image) | |
| encoded_img = MaxPooling2D((2,2),padding='same')(encoded_img) | |
| encoded_img = Conv2D(64,(3,3),activation='relu',padding='same')(encoded_img) | |
| encoded_img = MaxPooling2D((2,2),padding='same')(encoded_img) | |
| encoded_img = Conv2D(32,(3,3),activation='relu',padding='same')(encoded_img) | |
| encoded_img = MaxPooling2D((2,2),padding='same')(encoded_img) | |
| combined_features = Add(name="add")([encoded_text,encoded_img]) | |
| combined_features = Flatten()(combined_features) | |
| combined_features= Dense(512)(combined_features) | |
| output = Dense(4,activation='softmax')(combined_features) | |
| two_branch = Model([Input_text,Input_image],output) | |
| two_branch.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', | |
| optimizer='adadelta', metrics=['accuracy']) | |
| print(two_branch.summary()) | |
| plot_model(two_branch,to_file='./model_image/two_branch.png',show_shapes=True) | |
| Image(filename='./model_image/two_branch.png') | |
| two_branch.fit([x_train,image_data],label,batch_size=32,epochs=100,validation_data=([x_test,image_data_test],label_2),shuffle=True) | |
| two_branch.save_weights("./weights_saved/two_branch.h5") |
P
Pengyuan Liu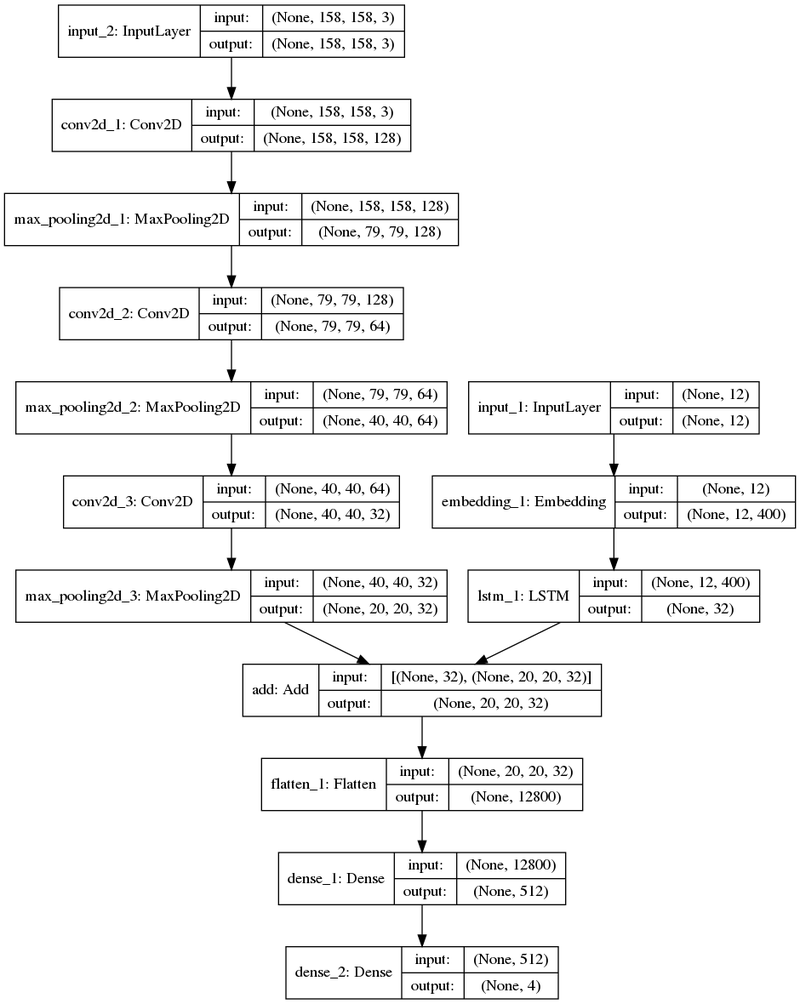
Neural network model
P
Pengyuan LiuSpaceApps is a NASA incubator innovation program.