Marcianos | Make Sense Out of Mars
Team Updates
Solution proposal
In order to solve this problem and allow the human being to explore Mars, a set was created that monitors the radiation of the environment and protects it from this radiation. For this, the various sensors and materials that could be used to construct the assembly were investigated. This step was the heart of the solution, because they are fundamental points for it to be viable.
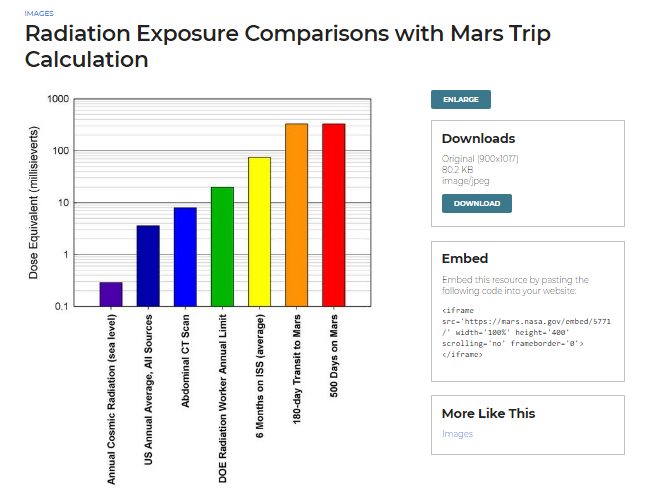
The research carried out from the beginning of the idea until the conclusion of the idea was extensive through the multidisciplinarity of areas such as physics, chemistry, engineering, nanotechnology and others. It was calculated from NASA data the amount of radiation received per day on this trip to avoid that level exceeding the safety level stipulated for the tissues of the human body.
With this information, first was defined and measured form, which are sensors already used in environments on Earth subjected to ionizing radiation (nuclear power plants, radioactive waste, etc.). Specifically, the active ionization chamber sensor was defined, which is a precise shape with an excellent reading range and adaptable to the proposal.
To carry out the protection of the human being, a nanomaterial called metal foam will be used, which will be responsible for composing the filling of a new suit, which will be used by the human being on Mars. This form of foam structuring results in low density, high strength, low coefficient of thermal expansion, extreme lightness and flexibility, and still has great capacity to withstand deformations and absorb energy. This material is in research and was discovered in 2015, it in addition to various mechanical properties possesses the property of interest which is to totally block certain types of radiation. In this way, a protective suit capable of allowing the man to remain in the environment of the red planet can be constructed. And as a form of safety, the sensor will monitor the possible radiation levels and, if there is something unexpected, the sensor can warn about this possible danger to the human being, allowing it to take shelter from the danger.
Solution proposalIn order to solve this problem and allow the human being to explore Mars, a set was created that monitors the radiation of the environment and protects it from this radiation. For this, the various sensors and materials that could be used to construct the assembly were investigated. This step was the heart of the solution, because they are fundamental points for it to be viable.The research carried out from the beginning of the idea until the conclusion of the idea was extensive through the multidisciplinarity of areas such as physics, chemistry, engineering, nanotechnology and others. It was calculated from NASA data the amount of radiation received per day on this trip to avoid that level exceeding the safety level stipulated for the tissues of the human body.With this information, first was defined and measured form, which are sensors already used in environments on Earth subjected to ionizing radiation (nuclear power plants, radioactive waste, etc.). Specifically, the active ionization chamber sensor was defined, which is a precise shape with an excellent reading range and adaptable to the proposal.
To carry out the protection of the human being, a nanomaterial called metal foam will be used, which will be responsible for composing the filling of a new suit, which will be used by the human being on Mars. This form of foam structuring results in low density, high strength, low coefficient of thermal expansion, extreme lightness and flexibility, and still has great capacity to withstand deformations and absorb energy. This material is in research and was discovered in 2015, it in addition to various mechanical properties possesses the property of interest which is to totally block certain types of radiation. In this way, a protective suit capable of allowing the man to remain in the environment of the red planet can be constructed. And as a form of safety, the sensor will monitor the possible radiation levels and, if there is something unexpected, the sensor can warn about this possible danger to the human being, allowing it to take shelter from the danger.

Proposta de solução
Com o intuito em solucionar esse problema e permitir que o ser humano possa explorar Marte, foi elaborado um conjunto que monitore a radiação do ambiente e o proteja dessa radiação. Para isso foram pesquisados os diversos sensores e materiais que poderiam ser usados para a construção do conjunto. Essa etapa foi o coração da solução, pois são pontos fundamentais para que a mesma seja viável.
A pesquisa realizada desde o início da ideia até a conclusão da mesma foi extensa passando pela multidisciplinaridade de áreas como física, química, engenharia, nanotecnologia entre outras. Calculou-se a partir dos dados da NASA a quantidade de radiação recebida por dia nessa viagem, para evitar que esse nível exceda o nível de segurança estipulado para os tecidos do corpo humano.
Com essas informações, primeiro foi definida e forma de medição, que são sensores já utilizados em ambientes na Terra sujeitos a radiação ionizante (usinas nucleares, lixo radioativos, etc.). Especificamente, foi definido o sensor ativo de câmara de ionização que é uma forma precisa e com excelente faixa de leitura e adaptável à proposta.
Para realizar a proteção do ser humano, será utilizado um nanomaterial chamado espuma de metal, que será responsável por compor o preenchimento de um novo traje, que será utilizado pelo ser humano em Marte. Essa forma de estruturação da espuma resulta em baixa densidade, alta resistência, baixo coeficiente de expansão termal, extrema leveza e flexibilidade, e ainda possui grande capacidade de suportar deformações e absorver energia. Este material está em pesquisa e foi descoberto em 2015, ele além de diversas propriedades mecânicas possui a propriedade de interesse que é a de bloquear totalmente determinados tipos de radiação. Desta forma, poderá ser construído um traje protetor capaz de permitir que o homem possa permanecer a no ambiente do planeta vermelho. E como forma de segurança, o sensor irá monitorar os níveis de radiação possíveis e assim, caso haja algo não esperado, o sensor pode alertar sobre esse possível perigo para o ser humano, permitindo que o mesmo se abrigue do perigo.
Definição do problema
Após os estudos, a condição escolhida para a solução foi o nível de radiação nociva existente em Marte. A Nasa possui uma base de dados que estima a quantidade de radiação para uma viagem de 830 dias (180 dias de ida, 500 dias de estadia e 180 dias de volta). Conforme os estudos, percebeu-se que são níveis que um ser humano não suporta e, consequentemente, morreria se exposto a essa radiação em Marte.
Marte possui índices de radiação bem maiores que os da Terra, por isso este ponto merece grande atenção para que haja a possibilidade de estadia no planeta. A radiação em questão trata-se da radiação ionizante, que pode ocasionar efeitos nocivos ao ser humano, pois ao interagir com os materiais ela arranca matéria destes.
Em aspectos biológicos, os tecidos do corpo humano possuem grandes sensibilidades a determinadas doses de radiação ionizante. Essa interação pode causar danos irreparáveis como destruição de células, câncer, ou até mesmo a morte da pessoa, dependendo da dose absorvida.

Definição do Tema
Após leitura dos temas e desafios propostos, o grupo fez uma reunião para definir qual seria o desafio escolhido. Foram definidos quais os pontos de maior relevância conforme as considerações de cada desafio. Então, foi definido qual o tema para o qual a solução seria proposta. O tema escolhido foi o “Faça sentido em Marte”. A partir disso, foram feitos diversos estudos sobre as condições existente em Marte, como: clima, gravidade, solo, atmosfera, níveis de radiação, geologia, localização, etc.
SpaceApps is a NASA incubator innovation program.