No G, no problems | Design by Nature
The Challenge | Design by Nature
Space Inspector Gadget
Space Inspector Gadget is a free flying autonomous drone that detects damage from micrometeoroids and orbital debris to the external body of space craft
What is the problem?
Spacecraft that will travel to and beyond the moon face a high risk from MMOD impacts. Limited communication to Earth and limited image downlink means ground control of inspection tools is challenging. Analysis of all inspection images on Earth means more ground crews and longer timelines to reach decisions. Control from in-space crews on future spacecraft or space stations use precious crew time and robotic manipulator time as well. Therefore, an autonomous inspection and damage detection system is required for future spaceflight missions.
What are the requirements?
- System must be as light and as small as possible
- System must be capable of reliably operating in orbital / deep space conditions
- System must be able to identify damage to spacecraft and assess the level of risk to the integrity of the spacecraft.
- System should be capable of conducting inspection operations autonomously
Operating Conditions:
- Earth Orbit / Deep Space - High/Low Temperature, Low Pressure (-100 to 120 degree celsius)
- Hypersonic micro-projectile impacts
- Low lighting/ high lighting conditions
- Micro/Zero gravity
Inspection Routine
The free-flyer(s) will circle around the spacecraft (in a spiraling way) at a distance from the spacecraft so it can observe more area at once, then once it perceives damage it will go closer to the spacecraft where it will take photos and measure the depth of the dent caused by the debris.
MMOD Damage Detection
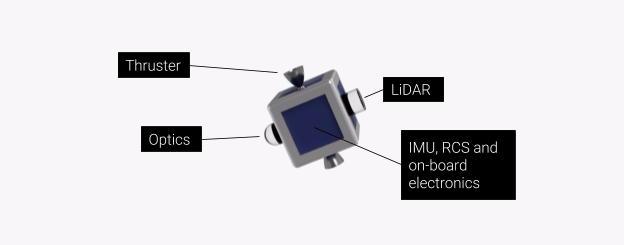
- Optical
- LiDAR
Using LiDAR, the free flyer will be able to map the surface of the mothership. When it observes abnormalities on the surface, it will dock near the damaged surface (using geckskin adhesive) for a detailed analysis of the hole/scratch/dent. This would include exact diameter of the hole, length of the crack/scratch and depth of the hole. Using elementary threat analysis, the flyer should be able to categorise the threat as serious or trivial. If the threat is serious, the engineers on board can be alerted. The flyer will then resume its circuit of the mother ship. The path is defined based on the design of the spacecraft it is being used on.
How does it analyse data?
- Using image processing.
- The information is relayed wirelessly to a central computer aboard the spaceship for processing. . This is where the main threat analysis is done, using trained neural networks. It makes sense to put the mainframe on the main ship and not on the flyer considering that the flyer can get damaged and so the flyer itself can be replaced at a lower cost. It is for the same reason we make the flyer modular.
How will it measure the depth?
- Ultrasound
- LiDAR
Propulsion and Attitude Control
Bi-directional monopropellant or cold-gas thrusters for accelerating and decelerating in one dimension. Reaction wheels for attitude control. Effectively 6 Degrees of Freedom.
Power Source
Batteries / Solar Panels
What material should the exterior be made from?
A light polymer or metal that is heat and cold resistant (394-173 Kelvin)
(Whittle shield)
- Kevlar
- Aluminium alloy
Bio-Inspiration?
- Gecko skin
- Neural networks
What value are we adding compared to existing solutions?
- It will be autonomous, meaning no or less time wasted by astronauts inspecting
- Free-flyer gives more regions of freedom
- Improve safety checks, the Inspector is capable of detecting small damages by MMOD that the existing technology usually overlooks.
Who’s our customer?
- Spacecraft operators (NASA, ESA, SpaceX)
What are the costs involved?
- Research and Development
- Manufacturing
- Marketing
What are the next steps?
- Get expert engineers for R&D
- Get resources to manufacture
- Introducing a repair function to make manual repairs obsolete
SpaceApps is a NASA incubator innovation program.